Unique models adopted by Li-ion Battery Recycling Start-Ups – investigated by IDTechEx
01.02.2022Unlike typical product exchange business models, recycling is more complex. It provides a service that not only results in a material product but also positive externalities associated with reduced landfilling and sustainable material recovery. For Li-ion battery recycling, this means less unsustainable mining and a reduction in the transportation distance of battery metals due to recycling creating domestic supply chains.
© IDTechEx
IDTechEx have identified a variety of business models adopted by recyclers. Some aim to optimize the transport and collection pathways, via Spoke and Hub or mobile solutions, while others look to license their technologies or sell recycling products. The new IDTechEx report, “Li-ion Battery Recycling Market 2022 – 2042”, presents a detailed analysis of the current value chain following the analysis of over 85 Li-ion battery recyclers globally.
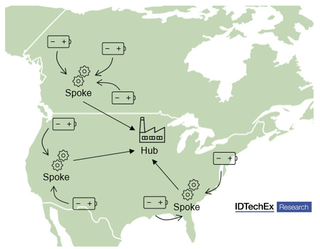
Sustainability is a key driver for Li-ion battery recycling, so it is important that every aspect of a recycler’s activity is optimized for minimum environmental impact and maximum efficiency. The spoke and hub model for Li-ion battery recycling has separate facilities for mechanical recycling and refining. Smaller ‘spoke’ plants are where end-of-life Li-ion batteries are broken down into black mass, which is then transported to the centrally located ‘hub’ plants for hydrometallurgical processing into battery materials. This system has the benefit of more distributed, accessible collection points which enable hazardous battery waste to be processed into a material that is easier to transport while allowing larger hub plants to develop economies of scale. The most efficient models will co-locate hub plants with battery manufacturing partners to reduce the material traveling distance and associated emissions.
Li-Cycle is a Li-ion recycling start-up that has adopted this model. The Canadian company currently operates two spoke plants in Ontario and Rochester, New York, and has planned to build a further two in the US. Li-Cycle’s first hub plant is expected to begin operation in 2023. Lithion Recycling is another Li-ion battery recycling start-up capitalizing on the benefits of a spoke and hub model and plan to build a first spoke plant to be operational by the end of 2022. Although the model creates greater feedstock access and reduces transport distances of hazardous material, a weakness is that it requires a balance between the hub and spoke activities and these early-stage companies may need to make flexible partnerships with companies willing to purchase black mass if spoke capacity exceeds hub.
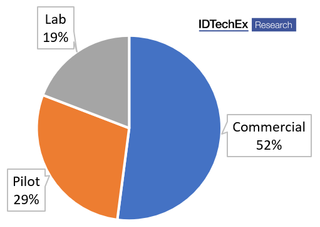 2022 share of Li-ion battery recyclers by scale
2022 share of Li-ion battery recyclers by scale
© IDTechEx
A further way of optimizing the accessibility of Li-ion battery recycling is allowing the process to come to the feedstock. This is being developed by Redivivus, a US-based start-up that has developed a mobile mechanical recycling process called ‘Redi-Shred’. Redi-Shred consists of a truck that shreds and neutralizes Li-ion batteries on-site to produce black mass which can be safely transported without additional hazmat costs. Redivivus plan to combine this technology with ‘Redi-cycle’, their hydro-electro refining process, to collect and refine Li-ion batteries on a commercial level. The strengths of this model include the emphasis on safety. End-of-life Li-ion battery suppliers are likely to be attracted to the service’s ability to neutralize the hazardous material on-site. Conversely, employing only mobile mechanical recycling services may limit capacity, especially as electric vehicle batteries become available on a large scale after 2030.
Recent IDTechEx research has determined that 48 % of Li-ion battery recyclers are currently operating on a lab- or pilot scale. This is reflective of innovators recognizing the value of recycling in the future circular economy and looking to improve the environmental credentials of electric vehicles. Throughout the 2020s, IDTechEx expects to see numerous Li-ion battery recycling start-ups transition to commercial-scale as global capacity increases to anticipate the availability of end-of-life electric vehicle batteries. For further details of the current Li-ion battery recycling market and future projections, consult the new IDTechEx report “Li-ion Battery Recycling Market 2022 – 2042”.



